Description
CONTENTS
PART A – EMPLOYABILITY SKILLS
UNIT I
1. COMMUNICATION SKILLS-III -3-19
1.1 Introduction to Communication – 3
1.2 Verbal Communication – 5
1.3 Non-Verbal Communication – 6
1.4 Pronunciation Basics – 9
1.5 Communication Styles – 10
1.6 Say No—Refusal Skills – 12
1.7 Writing Skills—Sentences – 16
1.8 Greetings and Introduction – 17
1.9 Introducing Yourself and Others – 18
1.10 Talking about family – 19
UNIT II
2. SELF-MANAGEMENT SKILLS-III – 20-27
2.1 Demonstrate Impressive appearance and Grooming – 20
Good Personal Hygiene Habits – 21
2.2 Demonstrate Teamwork Skills – 22
2.3 Networking Skills – 22
2.4 Self-Motivation – 23
2.5 Apply Time Management Strategies and Techniques – 24
2.6 Goal Settings – 25
UNIT III
3. ICT SKILLS-III – 28-63
3.1 Creating A Document In Word Processor – 28
3.2. Working with Text – 37
3.3 Formatting – 42
3.4 Working with Tables – 54
UNIT IV
4. ENTREPRENEURSHIP SKILLS-III – 64-70
4.1 Describe the Significance of Entrepreneurial valueS – 64
4.2 Attitude – 67
4.3 Thinking like an Entrepreneur – 67
4.4 Coming up with a Business Idea – 68
4.5 Form a Business Idea – 68
4.6 Understanding the Market – 69
UNIT V
5. GREEN SKILLS-III – 71-80
5.1 Define Green Economy – 71
5.2 Policies for a Green Economy – 73
5.3 Stakeholders in Green Economy – 74
5.4 Government and Private Agencies – 77
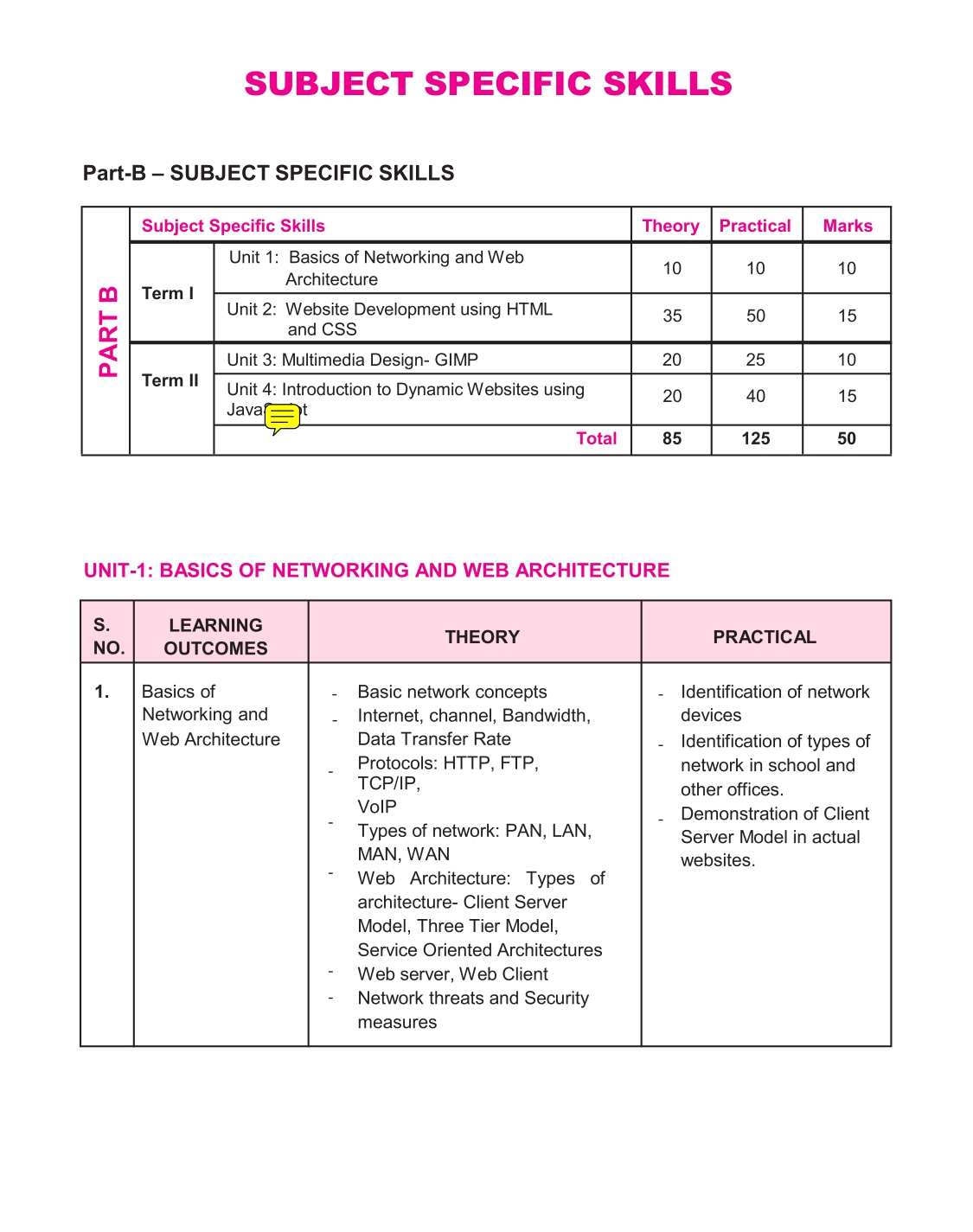
PART B – SUBJECT SPECIFIC SKILLS
UNIT I
1. BASICS OF NETWORKING AND WEB ARCHITECTURE – 3-54
1.1 Introduction – 3
1.1.1 Internet – 3
1.1.2 Invention of Internet – 41.2 Network Concept – 5
1.2.1 Advantages of Networking – 5
1.2.2 Elements required for network connections – 6
1.2.3 Some important terms used in Networking – 6
1.2.4 Switching techniques – 7
1.2.5 Types of Networks – 8
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) – 10
WAN (Wide Area Network) – 11
Characteristics of WAN – 11
Advantages/Disadvantages of WAN – 11
PAN (Personal Area Network) – 12
Characteristics of PAN – 12
Advantages/Disadvantages of PAN – 12
1.2.6 Transmission Media – 13
1.3 Network Topologies – 14
1.3.1 Bus Topology – 15
1.3.2 Star Topology – 15
1.3.3 Ring Topology – 16
1.3.4 Mesh Topology – 17
1.3.5 Tree Topology – 18
1.3.6 Hybrid Topology – 18
1.4 Network Devices – 19
1.4.1 Repeater – 20
1.4.2 Router – 20
1.4.3 Modem (Modulator Demodulator) – 21
1.4.4 Network Interface Cards or Ethernet card – 21
1.4.5 Hub – 21
1.4.6 Switch – 22
1.4.7 RJ45 Connector – 22
1.4.8 Gateway – 22
1.4.9 Bridge – 23
1.4.10 Wi-Fi Card (Wireless Network Card) – 23
1.5 Network Protocols – 24
1.5.1 Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) – 24
1.5.2 Internet Protocol (IP) – 24
1.5.3 Point – to – Point Protocol (PPP) – 25
1.5.4 HTTP – 25
1.5.5 HTTPS – 25
1.5.6 File Transfer Protocol (FTP) – 26
1.5.7 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) – 26
1.5.8 Post Office Protocol (POP) – 26
1.5.9 Telnet – 27
1.5.10 Internet Relay Chat (IRC) – 27
1.5.11 VoIP – 27
1.6 Web Architecture – 28
1.6.1 Client–server model – 28
1.6.2 Three-tier model – 29
1.6.3 Service-oriented architectures (SOA) – 29
1.6.4 MAC Address – 30
1.6.5 IP Address – 31
1.6.6 Web or World Wide Web – 31
1.6.7 Domain Name – 31
1.6.8 URL – 32
1.6.9 Email – 33
1.6.10 Website – 34
1.6.11 Web Servers – 36
1.6.12 Web Hosting or hosting a website – 36
1.6.13 Web Browser – 36
1.6.14 Browser Settings – 37
1.6.15 Add-ons and plug-ins – 38
1.6.16 Cookies – 38
1.7 Network Threats – 39
1.7.1 Malwares – 39
1.7.2 Eavesdropping – 41
1.7.3 Denial of Service – 41
1.7.4 Phishing – 41
1.7.5 Cyber Crime – 42
1.8 Network Security Tools and Services – 42
1.8.1 Firewalls – 42
1.8.2 Antivirus – 43
1.8.3 Password managers – 43
1.8.4 Cyber Law – 44
1.8.5 Intellectual property rights (IPR) Issues – 44
UNIT II WEBSITE DEVELOPMENT USING HTML AND CSS
2. STARTED WITH HTML – 55-122
2.1 Introduction – 58
A brief History – 58
Evolution of HTML – 59
2.2 HTML – OVERVIEW – 60
Text/HTML Editors – 60
Web Browsers – 60
2.3 HTML Tags – 61
Physical Tags – 61
Logical Tags – 61
2.4 Structure of an HTML Document – 61
HTML Documents – 61
Elements – 62
Attributes – 62
Creating, Saving and Viewing HTML Documents – 63
2.5 Editing an HTML Document – 63
2.6 Formatting HTML- 64
2.7 HTML Background – 76
2.8 HTML – Colors – 78
2.9 Linking in HTML – 81
2.10 Creating Lists with HTML – 85
2.11 EMBEDDING MULTIMEDIA IN WEB PAGES – 92
2.12 HTML Table – 97
2.13 HTML Frames – 99
2.14 HTML Forms – 101
3. CASCADING STYLE SHEET (CSS) – 123-158
3.1. Introduction – 123
3.2 Three ways to add styles to your Web Page: – 125
3.3. CSS – Syntax – 132
3.4 Comments in CSS – 138
3.5 CSS Properties – 138
4. PUBLISHING YOUR WEBSITE OR WEBPAGE – 159-169
4.1 Introduction – 159
4.2 Domain Name System (DNS) – 159
4.3 DNS Service – 160
4.4 DNS Namespace (Name Architecture) – 160
4.5 DNS Server – 162
4.6 DNS Name Server – 163
4.7 DNS Resolution (working) Process – 164
4.8 Domain Registration Process – 165
4.9 Publishing the website – 166
UNIT III
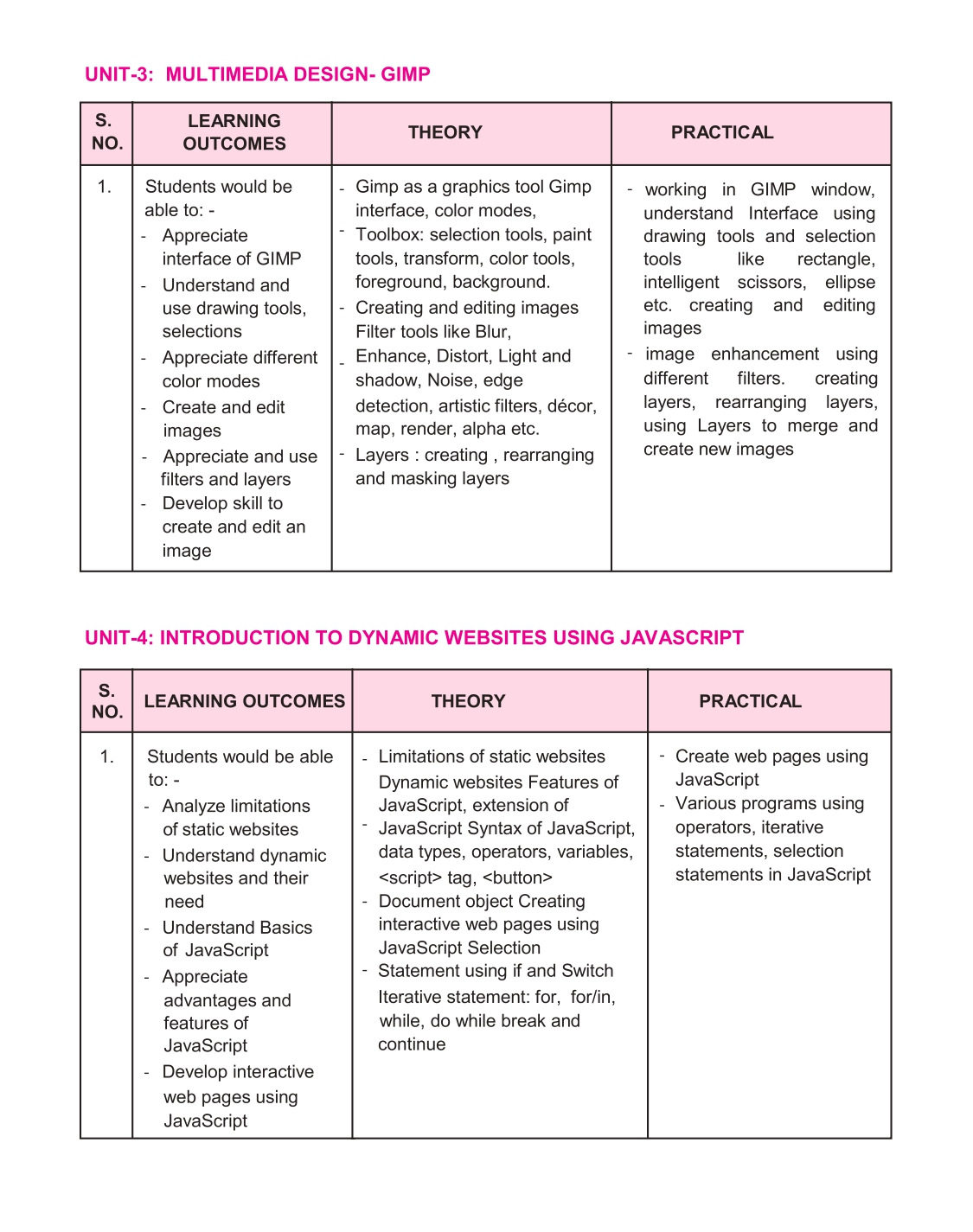
5. MULTIMEDIA DESIGN GIMP – 170-257
5.1 Multimedia – 170
Multimedia Design – 170
5.2 GIMP – 171
5.3 Install GIMP – 173
Pros and Cons of GIMP – 181
GIMP Tools – 181
Starting with GIMP – 182
5.4 Menus of GIMP – 183
5.4.1 File Menu – 183
5.4.2. Edit Menu – 188
Buffer – 191
Clear – 191
5.4.3 Select Menu – 194
5.4.4 View Menu – 198
5.4.5 Image Menu – 203
5.4.6 Layers – 210
5.4.7 Colors Menu – 216
5.4.8 Tools Menu – 224
5.4.9 Transform Tools – 236
5.4.10. Other Tools – 240
Paths Tools – 241
Text Tool – 241
Color Picker Tool – 241
Zoom Tool – 242
Measure Tool – 242
Filters – 242
UNIT IV
6. INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC WEBSITES USING JAVASCRIPT – 258-336
6.1 Introduction – 258
JavaScript Overview – 258
6.2 Enabling JavaScript in Browsers – 268
6.3 Code Structure in JavaScript – 269
JavaScript Syntax Rules – 271
Data Types, Variables and Operators – 276
6.4 JavaScript Data Types – 279
6.5 JavaScript Operators – 280
6.6 Dialog Boxes – 302
6.7. Control Statements – 305
6.8 Switch Statement – 311
6.9. Iterative or Looping Statements – 316










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.